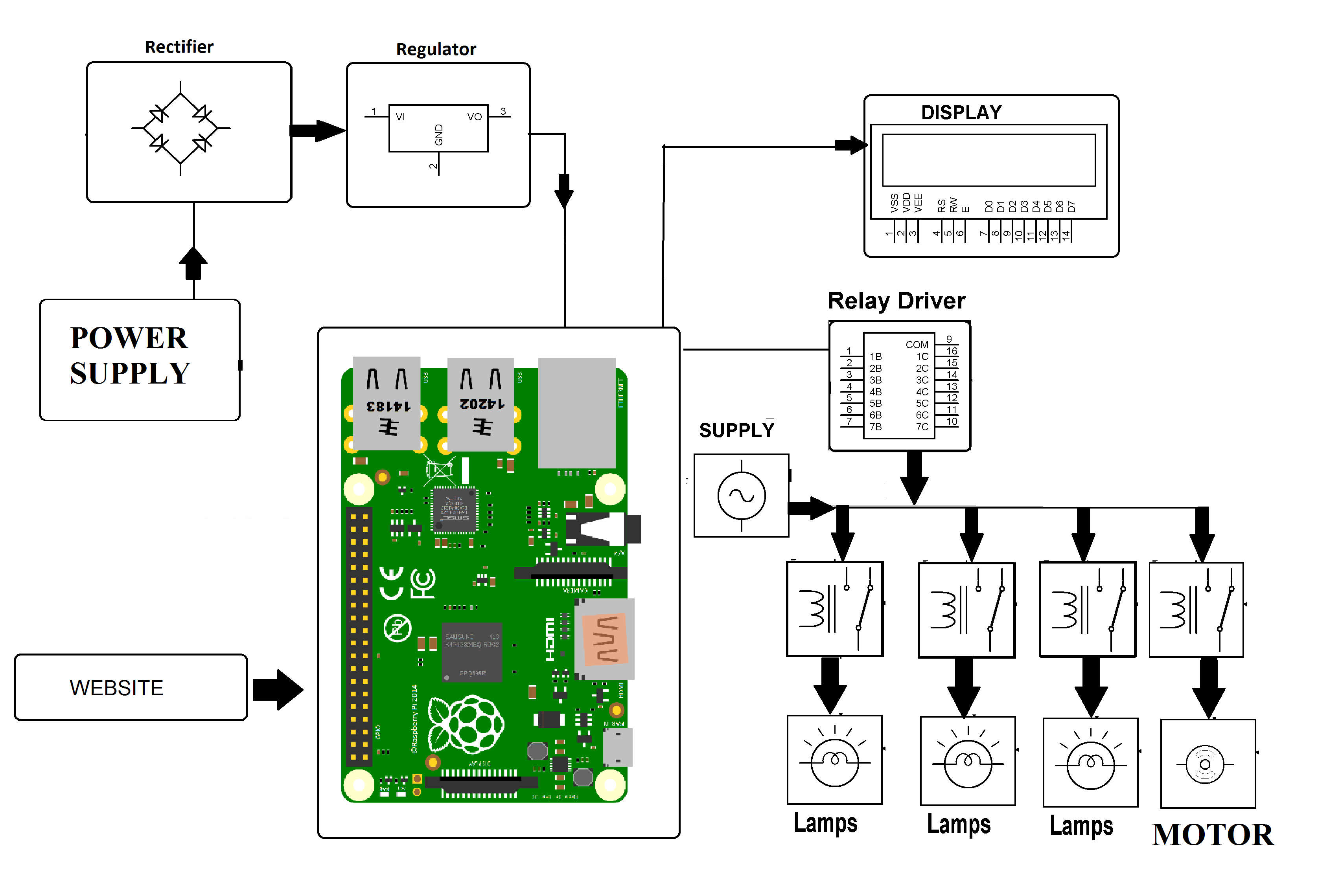
Ever found yourself miles away from your Raspberry Pi project, desperately needing to tweak a setting or monitor its progress? It doesn't have to be a logistical nightmare! With the right methodologies and software, remotely accessing your Raspberry Pi for remote IoT free download becomes not only possible but surprisingly straightforward, empowering you to manage your digital endeavors from virtually any location. This comprehensive guide serves as your roadmap to seamless remote control.
The notion of being tethered to your physical workspace to manage your Raspberry Pi is rapidly becoming a relic of the past. The evolution of technology has democratized access, making it possible for anyone, regardless of their technical expertise, to harness the power of remote control. This means you can now oversee your Internet of Things (IoT) devices and your Raspberry Pi from any point on the planet, significantly boosting efficiency and enabling a whole new realm of applications.
The implications are far-reaching, stretching from the automation of your domestic environment to the constant supervision of remote sensors crucial for scientific research or industrial operations. The ability to remotely access Raspberry Pi for remote IoT free download has triggered a paradigm shift in how we interact with and leverage technology. We will delve into the necessary techniques, explore indispensable tools, and offer invaluable tips to facilitate the establishment of remote access without incurring significant financial burdens.
- Bronwin Aurora Nude A Comprehensive Exploration
- Ari Kytsya Onlyfans A Comprehensive Look Into Her Career And Success
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Raspberry Pi (Model 4 B) |
| Type | Single-Board Computer |
| Manufacturer | Raspberry Pi Foundation |
| Release Date | June 2019 |
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2711, quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5GHz |
| Memory | 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4 SDRAM |
| Connectivity | 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz IEEE 802.11ac wireless, Bluetooth 5.0, Gigabit Ethernet, 2 USB 3.0 ports, 2 USB 2.0 ports, 2 micro-HDMI ports (up to 4Kp60 supported) |
| Operating System | Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian), Ubuntu, other Linux distributions, Windows 10 IoT Core |
| GPIO Pins | 40-pin GPIO header with various interfaces |
| Power Supply | 5V/3A via USB-C connector |
| Typical Applications | IoT projects, media servers, home automation, learning programming, retro gaming |
| Official Website | Raspberry Pi Foundation |
The idea is straightforward: your Raspberry Pi, once configured for remote accessibility, becomes a digital portal, ready to be summoned and manipulated at your command. When you remotely access Raspberry Pi for remote IoT free download, you're not simply managing hardwareyou're entering a realm of unlimited potential. Imagine controlling your home's lighting and temperature from a faraway beach, or analyzing data streamed from environmental sensors nestled deep within a forest. The breadth of applications is genuinely staggering, limited only by your imagination.
The benefits of remote access extend far beyond mere convenience; it represents a leap forward in efficiency. Imagine a scenario where a critical sensor malfunctions within a sprawling industrial complex. Instead of dispatching a technician on-site, you can remotely diagnose the issue, implement a temporary fix, and potentially prevent a costly shutdown, all without leaving your office. Similarly, picture updating your sophisticated home security system while vacationing abroad, ensuring your property remains protected, no matter your location. This is the transformative power of remote access in action.
Before delving into the specifics of remote access, it's essential to appreciate the fundamental characteristics that make the Raspberry Pi such a remarkable piece of technology. More than just a miniature computer, it's a gateway to innovation, a canvas for creating solutions to a wide array of problems.
- Unveiling The World Of Mms Video A Comprehensive Guide
- Sophie Rain Spiderman Video A Comprehensive Guide
The Raspberry Pi is a compact, economical computer that has found its niche in diverse applications, ranging from education in programming to the construction of sophisticated IoT ecosystems. Its appeal lies in its inherent versatility and affordability, making it a favored tool among both hobbyists exploring new ideas and seasoned professionals developing real-world applications.
Its key features include: a compact and portable design that allows for easy integration into various projects; versatility owing to its compatibility with multiple operating systems, expanding its usability in different environments; a wide array of GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins that facilitate seamless interaction with external hardware components; and a robust community that fosters knowledge sharing, provides support, and contributes to the development of invaluable resources.
The "Internet of Things" (IoT) is fundamentally about establishing connections between devices, enabling them to interact and share information intelligently. By integrating IoT principles with the remote accessibility of Raspberry Pi, you create a synergistic effect that amplifies capabilities, creating possibilities for you to relate to technology.
Benefits of using IoT for remote access include: enhanced operational efficiency in managing devices scattered across various locations; real-time monitoring and analysis of data collected from remote sensors, enabling proactive decision-making; cost-effective solutions, especially beneficial for large-scale deployments where minimizing physical intervention is crucial; and robust security and control mechanisms that ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your remote operations.
The process of configuring remote access for your Raspberry Pi might initially seem complex, but this step-by-step guide will help you navigate it. Following these instructions, youll be up and running in a short amount of time.
SSH, or Secure Shell, is the foundational protocol that enables secure remote communication with your Raspberry Pi. It ensures that all data transmitted between your device and the remote client is encrypted, protecting it from eavesdropping and unauthorized access. To enable SSH, open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi and type:
sudo raspi-config
This command launches the Raspberry Pi configuration tool. Navigate to the "Interface Options," select "SSH," and enable the service.
A dynamic IP address, assigned by your internet service provider, can change periodically, making it difficult to reliably connect to your Raspberry Pi remotely. A static IP address, on the other hand, remains constant, ensuring a stable connection point. There are two primary methods for setting up a static IP address. You can configure it directly through your router's settings, reserving a specific IP address for your Raspberry Pi based on its MAC address. Alternatively, you can configure it through the terminal on your Raspberry Pi by editing the /etc/dhcpcd.conf file. This method involves specifying the static IP address, gateway, and DNS server information.
Even with a static IP address, accessing your Raspberry Pi from outside your local network can be challenging if your external IP address changes. Dynamic DNS (DDNS) services provide a solution by associating a domain name with your dynamic IP address. When your IP address changes, the DDNS service automatically updates the domain name to point to the new address. Popular DDNS services include No-IP and DuckDNS. Setting up a DDNS service typically involves creating an account, selecting a domain name, and installing a client on your Raspberry Pi that periodically updates the IP address associated with the domain name.
Numerous tools are available that significantly simplify the process of establishing and managing remote access to your Raspberry Pi. Some of the most effective and user-friendly options include:
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) Viewer provides a graphical interface, allowing you to interact with your Raspberry Pi as if you were sitting in front of it. This is particularly useful for tasks that require visual interaction, such as running graphical applications or managing files through a desktop environment. VNC Viewer is readily available for various platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS, enabling you to connect from virtually any device.
TeamViewer offers a comprehensive remote access solution with a strong emphasis on ease of use and cross-platform compatibility. It allows you to remotely control your Raspberry Pi, transfer files, and even conduct online meetings. TeamViewer is particularly well-suited for users who require a simple and intuitive interface without extensive technical configuration.
Security should always be a paramount concern when setting up remote access. Without adequate security measures, your Raspberry Pi and your entire network become vulnerable to unauthorized access and malicious attacks. To minimize these risks, consider the following security best practices:
Employing strong, unique passwords for all user accounts on your Raspberry Pi is a fundamental security measure. Avoid using common words, personal information, or easily guessable patterns. Instead, opt for passwords that are at least 12 characters long and incorporate a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Additionally, avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts. A password manager can assist you in generating and storing strong, unique passwords.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification factor in addition to your password. This factor can be a code generated by an authenticator app on your smartphone, a security key, or a biometric scan. Enabling 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
Regularly updating your Raspberry Pi's operating system, software packages, and firmware is crucial for patching security vulnerabilities and ensuring that you have the latest security enhancements. Software updates often include fixes for newly discovered security flaws, making it essential to apply them promptly. You can update your Raspberry Pi's software by running the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgrade
Restricting access to your Raspberry Pi to only trusted devices and networks minimizes the attack surface and reduces the risk of unauthorized access. You can achieve this by configuring your firewall to allow connections only from specific IP addresses or networks. Additionally, consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your network traffic and mask your IP address, adding an extra layer of security when connecting remotely from untrusted networks.
The Raspberry Pi ecosystem thrives on open-source principles, which means that you can leverage a vast array of free software and resources to enhance your IoT projects. The following are some free software options.
Raspberry Pi OS, previously known as Raspbian, is the official operating system for the Raspberry Pi. It is a Debian-based Linux distribution optimized for the Raspberry Pi's hardware. Raspberry Pi OS is free to download and use, and it comes pre-installed with various useful tools and utilities, including a desktop environment, a web browser, and a terminal emulator.
Node-RED is a visual programming tool that simplifies the creation of IoT applications. It provides a browser-based flow editor that allows you to connect various nodes representing different devices, services, and functions. Node-RED is particularly well-suited for automating tasks and creating data flows between different systems. It is free to download and use, and it has a vibrant community that contributes to the development of new nodes and flows.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight messaging protocol widely used in IoT applications. It enables devices to communicate with each other and with a central server using a publish-subscribe model. MQTT is particularly well-suited for resource-constrained devices and networks with limited bandwidth. There are numerous free MQTT broker implementations available, such as Mosquitto, that you can use to set up your own MQTT server.
Even with careful planning and execution, issues can arise when setting up remote access. The following are some common problems and solutions:
First check your SSH settings and make sure the service is enabled. Also, check your IP address and firewall settings. Make sure that your Raspberry Pi and the device from which you are trying to connect are on the same network. Verify that the SSH port (default port 22) is open on your firewall.
Next optimize your network settings and think about using a wired connection instead of Wi-Fi for better performance. Reduce the resolution and color depth of your remote desktop session to minimize the amount of data being transmitted. Also close any unnecessary applications running on your Raspberry Pi to free up system resources.
Here are some expert tips to make your remote access experience smoother:
Back up your data. Make regular backups of your Raspberry Pi's data and configuration files. This will allow you to quickly restore your system in case of a hardware failure, software corruption, or security breach.
Document your setup process for future reference. Keep a record of all the steps you took to set up remote access, including configuration settings, software versions, and security measures. This documentation will be invaluable for troubleshooting problems and replicating your setup on other devices.
Lastly stay updated with the latest trends and technologies in IoT. The IoT landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, protocols, and security threats emerging all the time. Staying informed about these developments will enable you to adapt your remote access setup to maintain optimal performance and security.
- Best Remote Iot Vpc Ssh Raspberry Pi Free Setup Guide
- Odia Mms Video Unveiling The Truth Behind The Controversy